Monica Piccinini
27 September 2023
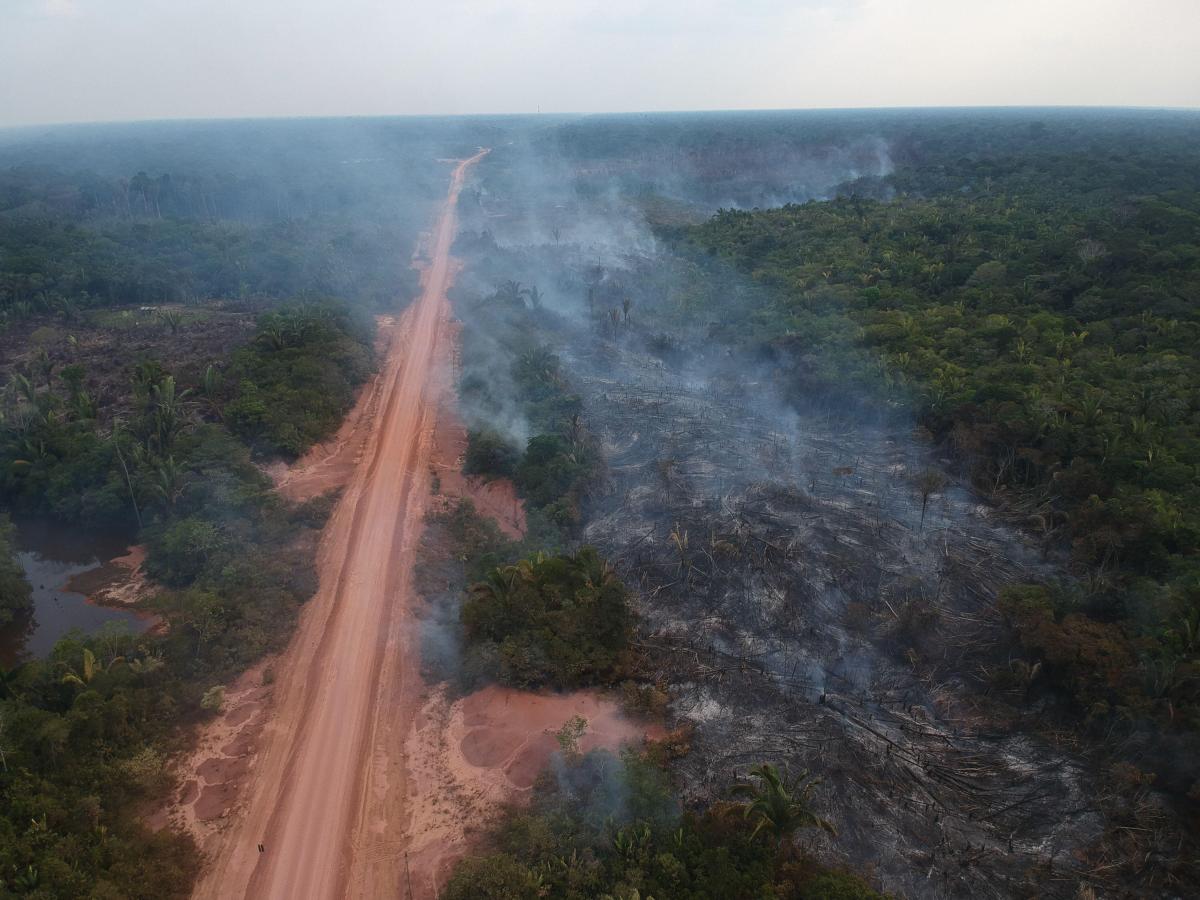
The reconstruction of Amazon’s BR-319 highway in Brazil, connecting the capital Manaus in central Amazonia to the southern edge of the forest, Porto Velho, is an ambitious and controversial infrastructure project, supported by many politicians and organisations, and a possible catalyst to further social and environmental degradation in the region.
The BR-319 highway project could result in increased illegal logging, violence, violations of indigenous rights, and catastrophic consequences to local communities and the environment, including irreversible deforestation, warn scientists.
Officially inaugurated in March 1976 during the era of the military dictatorship led by General Ernesto Geisel, BR-319 fell into a state of disrepair by 1980. In 2015, during Dilma Roussef’s administration, a proposal to revitalize BR-319 was put forth.

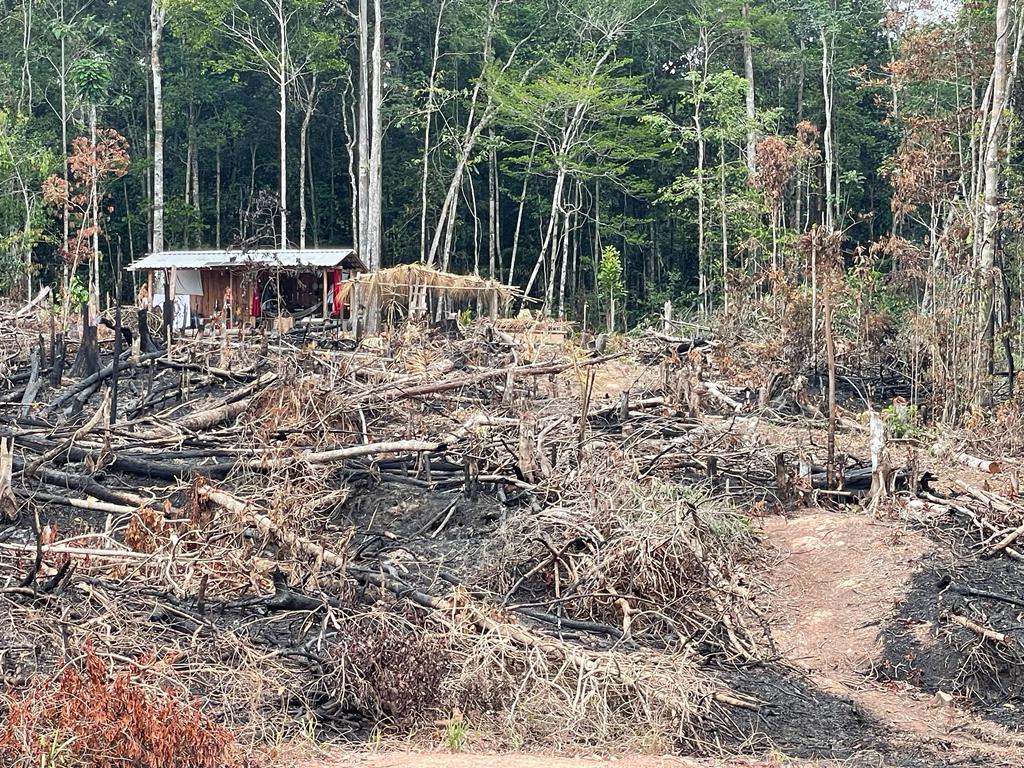
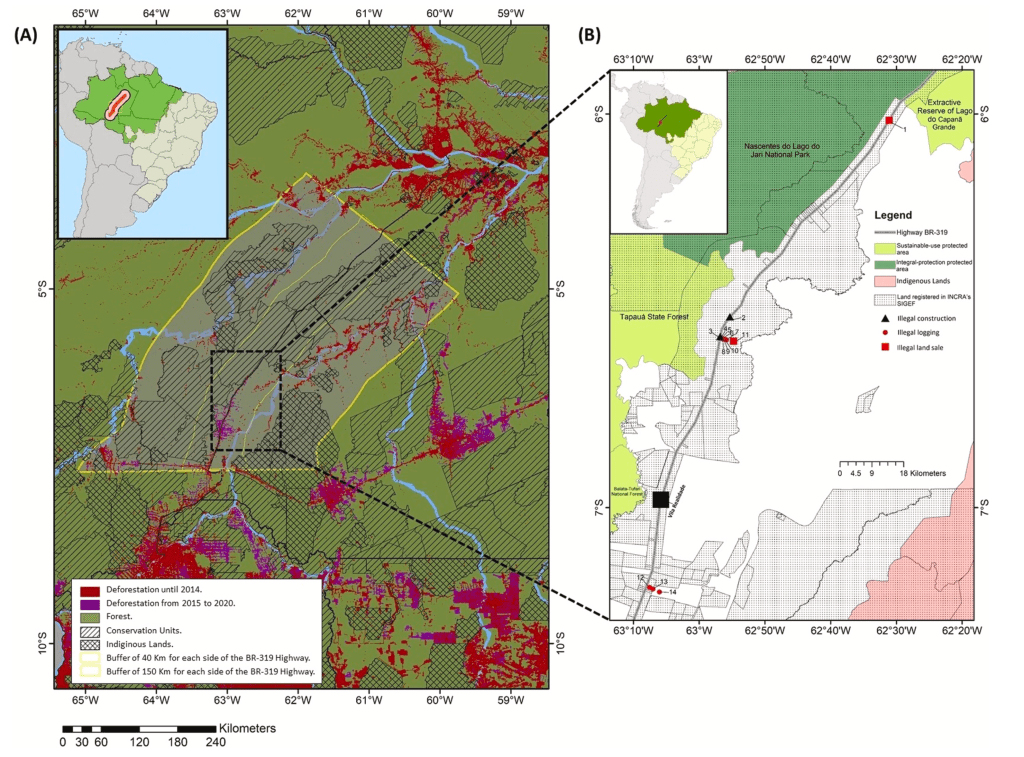
BR-319 highway, a stretch of 885.9 km, serves as an unguarded gateway to illicit side roads in areas with a high density of indigenous territories, legally designated reserves, and protected conservation areas. This accessibility grants illegal miners, loggers, settlers, and land invaders entry into untouched forest.
According to a study by scientists, Lucas Ferrante and Philip Fearnside, the reconstruction of BR-319 and the building of planned connecting roads would act as spearheads for deforestation and forest degradation in the western portion of the Brazilian Amazon.
“BR-319 highway cuts through one of the most preserved blocks of the forest, where it contains an enormous stock of carbon. This project is a threat to 63 indigenous lands and 18,000 indigenous people, not to mention the environment and biodiversity”, mentioned Ferrante.
In the Brazilian Amazon, a staggering 94% of deforestation happened in the vicinity of both official and native roads, vividly illustrating how highways are significant catalysts of deforestation.
A study by Ferrante and Fearnside suggests that BR-319 and its proposed planned side-roads will lead to a deforestation surge of over 1,200% in the region spanning from the highway to Brazil’s border with Peru, primarily in the central Amazon.
The Amazon rainforest plays a vital role in the regional and global climate system, acting as a carbon reservoir, aids in the dispersion of trace gases and aerosols, and is a crucial part of the water cycle. Its contribution of moisture to other regions is instrumental for maintaining hydrological stability on both regional and global scales.
Justifications
The primary justifications presented by the current government for repaving BR-319 highway involve improving access to healthcare and education in the region, in addition to addressing national security concerns.
“The highway actually increases disparities in public health, which also demystifies the justification for bringing healthcare to municipalities,” explained Ferrante.
According to Ferrante and Fearnside, the road is not a priority for “national security” because it is far from Brazil’s borders. This information was announced in 2012 by the Brazilian Army’s commander for Amazonia and not mentioned anywhere in the Brazilian military’s 2008 National Strategy for Defense.
While scientists have issued warnings about the potential adverse outcomes this project could have on the region, Brazil’s president, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, continues to view it as a top priority.
In June 2022, prior to his presidential election, Lula emphasised the significance of the highway for the economies of both Amazonas and Rondônia.
Last month, Brazil’s transport minister, Renan Filho, went as far as proposing the utilisation of the ‘Fundo Amazonia’ to finance the reconstruction of BR-319, which he dubbed as “the most environmentally friendly roadway on the planet.”
Scientists Expose Negative Impact

The potential consequences of reconstructing the BR-319 highway, including the risk of deforestation, could affect an area exceeding 300,000 square km within the Amazon, surpassing the size of São Paulo state, according to the result of a study conducted jointly by the CPI (Climate Policy Initiative)/PUC-Rio and the Amazônia 2030 project.
The researchers concluded that BR-319 highway’s impact is anticipated to affect a population of approximately 320,000 individuals in nine municipalities. Within the area of influence of BR-319 are also 49 indigenous territories, 49 conservation zones, and 140,000 square kilometers of publicly owned forests without designated purposes.
In his latest study, Fearnside revealed that by 2100, the reconstruction of BR-319 highway would increase deforestation not only around the highway, but also in the regions with roads directly connected to BR-319, by a staggering 60% in relation to deforestation in the projected scenario without reconstruction.
Amazonas road network connecting to BR-319 includes federal highways BR-174, BR-230, BR-174 and state highways AM-254 and AM-354.
There are additional planned projects to build highways connecting to BR-319, including AM-366, AM-360, AM-343 and AM-356. Some of these highways will reach one the most preserved areas in the Amazon, known as the “Trans-Purus” region.
The BR-319 highway reconstruction project is deficient in two essential aspects mandated by the law: firstly, it lacks an economic feasibility study, known as the EVTEA, as stipulated by Law 5917/1973. Secondly, it has failed to conduct the necessary consultations with indigenous communities, as required both by International Labour Organisation (ILO) Convention 169 and Brazilian law 10,088/2019.
Based on Ferrante’s assertion, supported by his research highlighted in the Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities,
“The deforestation occurring along the central stretch of the BR-319 highway has resulted in a rise in malaria cases by 400%. This serves as an indicator, underscoring the potential for environmental degradation driven by the BR-319 highway to contribute to the emergence of a new pandemic.”
The reopening of this highway would also enable agribusiness expansion into new territories, including activities such as cattle farming, soybean and palm oil cultivation, the expansion of monoculture for large-scale biofuel production, as well as meeting the needs of fossil fuel companies, hydroelectric dams, mining operations, and other industries.

Ferrante calls attention to the latest attempt in dismantling Brazil’s environmental agenda and how it may affect the area surrounding BR-319 highway:
“The recent changes made by the National Congress during Lula’s administration, which involved the reduction of environmental protection laws and the relocation of CAR (Brazil’s National Environmental Registry of Rural Properties) from the environment ministry, could lead to a further surge in deforestation within the BR-319 highway area. This initiative lacks the essential governance and environmental and economic viability required for the project.”
Ferrante delivers a final message to Lula’s government:
“Lula’s administration has consistently lacked a positive environmental track record and has more recently indicated its backing for the BR-319 highway reconstruction initiative. It is essential that the government reevaluates this unviable project and takes into consideration the advice of experts and the findings of scientific research.”
Article published in The Ecologist: https://theecologist.org/2023/sep/27/amazons-route-deforestation
Article published in The Canary: https://www.thecanary.co/global/world-analysis/2023/09/27/br-319-amazon-deforestation/











