Monica Piccinini
11 October 2023
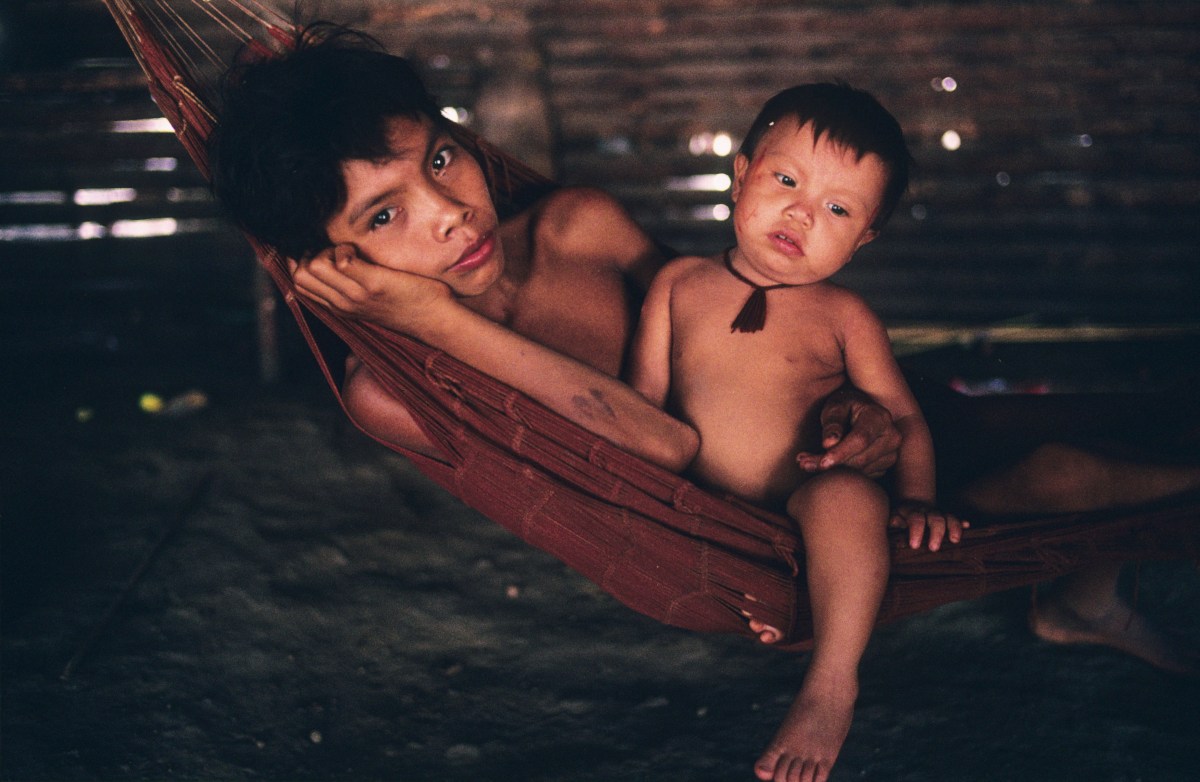
The Yanomami live in the rainforests of northern Brazil and southern Venezuela and are considered the largest isolated tribe in South America. The Brazilian state, corporations and illegal activities have for decades violated their rights and caused the deaths of countless Yanomami. However, they now face a growing new threat – from ultra-processed foods.
In the far northern region of Brazil, the Yanomami population consists of approximately 27,000 individuals, spread across more than 300 villages within the Yanomami indigenous territory, in an area of 9,664,975 hectares.
The health conditions afflicting the Yanonami community, including malnutrition and chronic diseases, are a result of the violation of their rights, unstable socio-economic conditions, and ongoing invasions of their territory. These circumstances have led to a social-environmental vulnerability within their population, placing their families, particularly children, at risk of consuming ultra-processed foods.
A study conducted by Brazil’s Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, Fiocruz, offers groundbreaking insights into the dietary patterns of Yanomami indigenous youth. It reveals that more than 90% of Yanomami aged 6 to 59 months exhibit short stature (linear growth stunting).
“Without a doubt, the Yanomami increased consumption of carbohydrates, sugar, salt, fat, food additives, and low-nutrient highly processed foods, contributes to nutritional and metabolic health concerns, specifically among their children,” explained Jesem Douglas Yamall Orellana, Fiocruz researcher of public health and epidemiologist at Fiocruz, and one of the authors of the study.
According to Orellana, the heightened consumption of ultra-processed foods among the Yanomami children not only significantly exacerbates their pre-existing health issues, but also gives rise to new ones.
Numerous research findings have established associations between ultra-processed foods and various health concerns, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, cancer, depression, multiple sclerosis (MS), cardiovascular disease, and even mortality.
Last month, Brazil’s national health council president, Fernando Zasso Pigatto, issued a recommendation with following note:
“Considering that, in the scenario of poverty and hunger, the Yanomami people are hostage to the supply of processed and ultra-processed products, in many cases expired, satisfying external interests, which worsens the scenario of infectious disease, malnutrition, deficiencies, nutritional and chronic diseases, such as the onset of diabetes, hypertension and obesity.”
Study Data
The study group reported that the minimally processed ‘regional’ foods consumed by the Yanomami consisted primarily of fruits (69%), followed by corn, roots, or tubers (45%), peach palm or palm heart (33%), fish or crab (33%), and couscous (32%), according to the most frequently mentioned items.
The ultra-processed foods most commonly mentioned were cakes or cookies (25%) and chocolate or chocolate powder (6%). Some also consume soft drinks, soda, candy, artificial juice and yogurt, canned foods, instant noodles, among other items.
The Fiocruz study was designed as a comprehensive survey for children residing in villages within three remote regions of the Brazilian Amazon, offering valuable data for this particularly under represented group.
The research group consisted of Yanomami children ranging from six months to five years old, and the investigation took place within three Yanomami communities located in the Brazilian Amazon: Maturaca, Ariabu, and Auaris.

The residents of Maturaca and Ariabu villages usually have more regular interactions with non-indigenous communities, which include military personnel, healthcare workers, illegal miners, loggers and criminal groups.
In contrast, the Ariabu population is relatively isolated, having limited contact with urban communities. Consequently, they enjoy greater territorial mobility, affording them the freedom to practice their traditional way of life.
The research findings indicated that the consumption of ultra-processed foods was significantly more prevalent in children from Maturaca (11.6 times higher) and Ariabu (9.2 times higher) in comparison to the children from Auaris.
This observation emphasises the importance of social contact with non-indigenous communities as a critical factor influencing the consumption of ultra-processed foods.
Another intriguing finding from the study was a 31% reduction in ultra-processed food consumption among children whose mothers had shorter stature when compared to those whose mothers had a proper height.
Orellana explained, “Typically, the most economically disadvantaged mothers in the community can be identified as those with higher short stature rates, limited or no income, a background of enduring poverty, and a history of hardships that have stunted their growth into ‘short adults.’ These mothers lack the means to purchase and access ultra-processed foods, which, in turn, works to their advantage.”
The general occurrence of ultra-processed foods stood at 32%, and this was linked to both the location of residence and the height of the mothers.
The Culprits
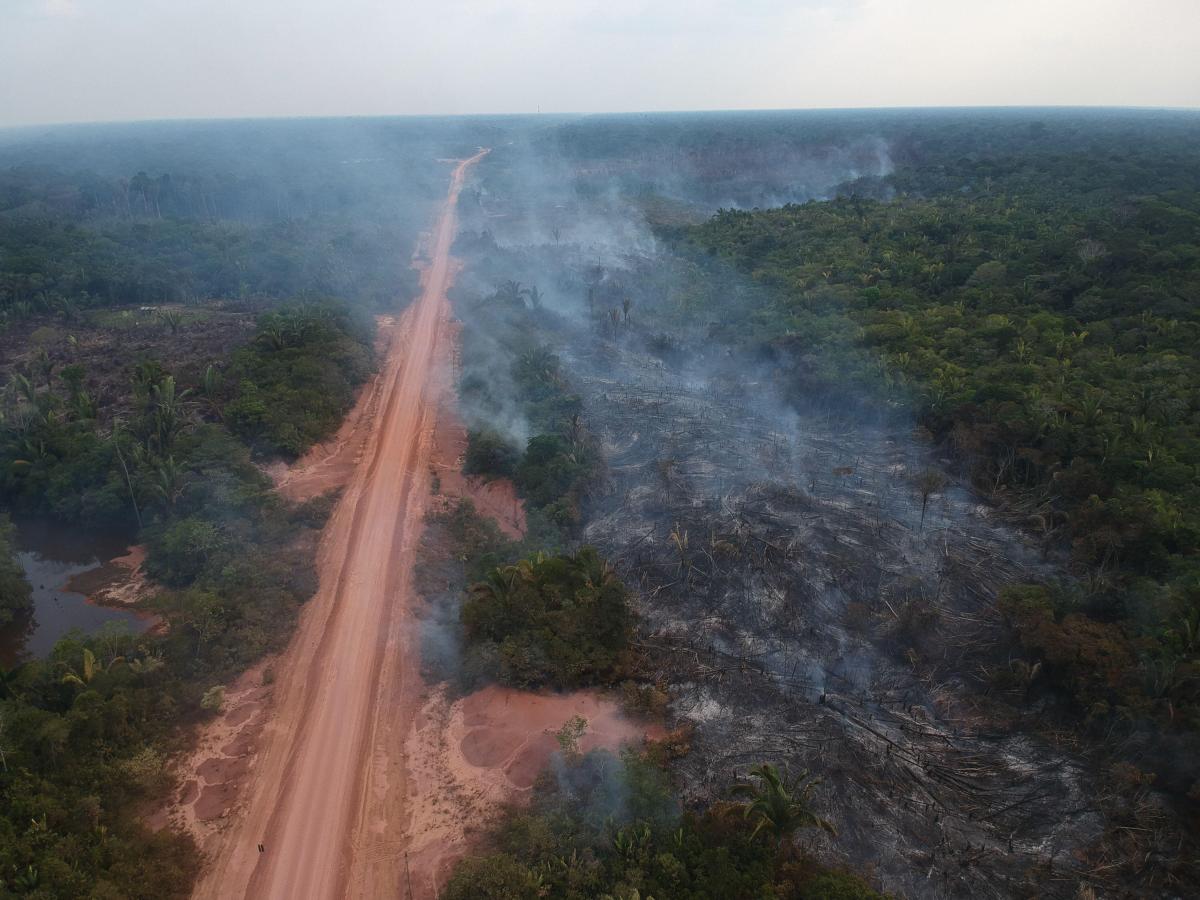
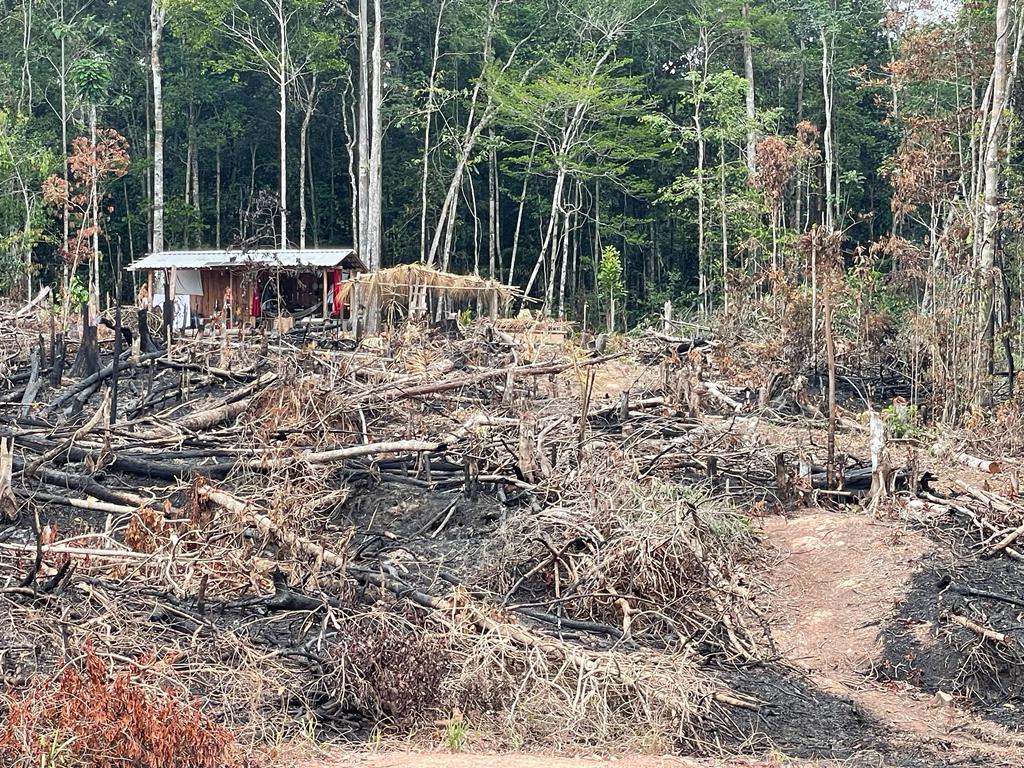
The Yanomami are traditionally categorised as hunter-gatherers, but the frequent invasions of illegal miners, loggers, and criminal organisations into their territory have a direct influence on the areas from which they gather their food, consequently affecting their dietary patterns.
Their families are compelled to interact with non-indigenous communities, resulting in their exposure to urban centers and the consumption of ultra-processed foods with poor nutritional content, high energy density, low fibre and micronutrient content, and an abundance of preservatives and industrial additives.
According to Orellana, what caught the interest of the group of scientists was the correlation between the increased consumption of ultra-processed foods by the Yanomami and a higher likelihood of them abandoning their agricultural practices.
“The Yanomami were historically known for their semi-nomadic lyfestyle, moving to new areas every two years to allow their previously occupied lands to regenerate. Nowadays, they are reluctant to leave their territory due to the invasion of illegal miners, loggers and drug traffickers, which has instilled fear in them about the possibility of violent attacks,” explained Orellana.
Orellana added, “The Yanomami traditionally relied on their understanding of sun and lunar cycles, as well as rain and drought patterns, to observe and manage soil and land dynamics. However, recent shifts in weather patterns, including extreme climate conditions, have disrupted their ability to accurately determine the optimal planting times for crops like corn and cassava.
“Furthermore, they now face concerns about fishing due to the contamination of their rivers by illegal mining activities, particularly the presence of mercury. These environmental challenges have led the Yanomami to increasingly rely on ultra-processed foods, as they find themselves struggling to maintain their traditional practices.”
The developments observed among the Yanomami over the past two decades is similar to the experiences of nearly all indigenous populations in Brazil that have been in direct contact with non-indigenous communities for over 50 years.
“In the last nine months, we’ve observed specific actions undertaken by the federal government to address issues in areas previously identified as housing various invaders, and these actions have received considerable media coverage,” mentioned Orellana.
He detailed how certain national issues are manipulated and exploited by both the government and the media to further their interests:
“Extensive operations were conducted in these areas (Yanonami territory), featuring visits by the president and ministers. Once these matters were no longer the focal point, attention shifted to a different region. These undertakings are often referred to as ‘political spectacles’ rather than genuinely impactful operations.”
Climate change and frequent invasions into the Yanomami land by illegal miners, loggers, and criminal groups are the primary factors that impact their diet, well-being, and traditional lifestyle, making them crucial determinants of their survival.
Orellana pointed out several potential measures that could effectively address some of the problems impacting the Yanonami community:
“Immediate action is essential to establish control over the territory and impose severe and efficient penalties on intruders. Without these measures in place, the issues affecting the Yanomami, such as increased consumption of high-processed foods due to the disruptions in their traditional agricultural practices, which is detrimental to their well-being and cultural heritage, will persist without resolution.”
Article published in The Ecologist: https://theecologist.org/2023/oct/12/indigenous-tribes-made-ill-processed-foods
Article published in The Canary: https://www.thecanary.co/global/2023/10/10/yanomami-people-brazil-ultra-processed-food/
Article published in Portuguese in A Escola Legal: https://aescolalegal.com.br/blog/2023/10/11/yanomami-envenenados/